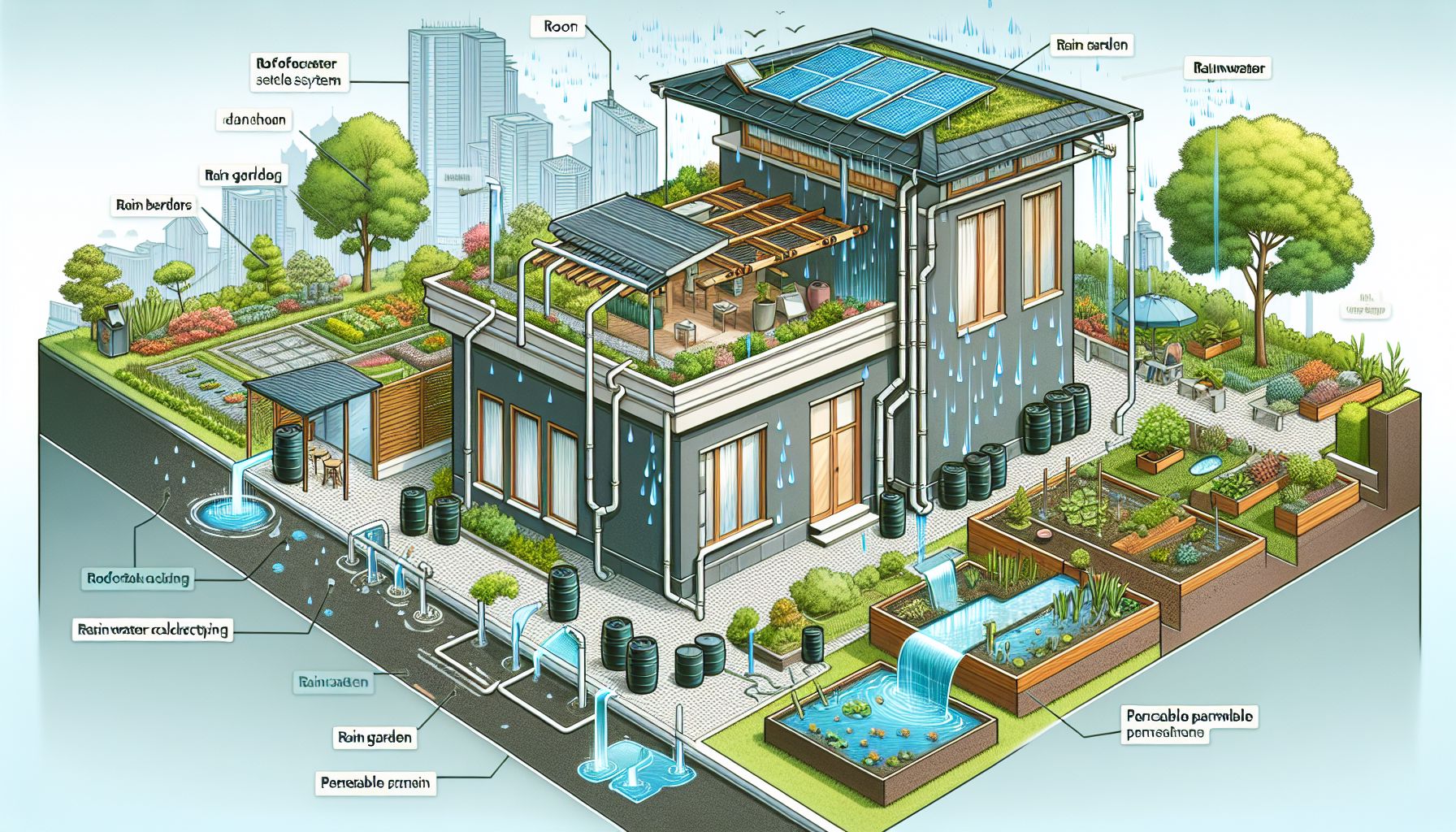
In recent years, the importance of sustainable water management practices has come to the forefront as water scarcity becomes an increasingly pressing issue globally. One of the solutions that have gained popularity is rainwater harvesting, especially in urban areas where water resources are often strained. Rainwater harvesting is the practice of collecting and storing rainwater for later use, reducing the demand on municipal water supply and decreasing runoff into storm drains. In this article, we will explore the various techniques for rainwater harvesting in urban households and the benefits it can bring.
Benefits of Rainwater Harvesting
-
Reduces Demand on Municipal Water Supply: By collecting rainwater for non-potable uses such as watering plants, washing cars, and flushing toilets, urban households can reduce their reliance on treated water from the municipal supply.
-
Mitigates Flooding: Rainwater harvesting helps to reduce runoff into storm drains, alleviating pressure on urban drainage systems during heavy rainfall and minimizing the risk of floods.
-
Cost Savings: Using rainwater for non-potable purposes can lead to cost savings on water bills, especially in regions with high water prices.
-
Promotes Self-Sufficiency: By harvesting rainwater, households can become more self-sufficient in terms of water supply, especially during periods of drought or water restrictions.
Techniques for Rainwater Harvesting
-
Rain Barrels: One of the simplest and most cost-effective methods of rainwater harvesting is to collect rainwater in barrels or tanks attached to downspouts from the roof. The collected rainwater can then be used for watering plants or other outdoor purposes.
-
Rainwater Tanks: Larger rainwater tanks can be installed underground or above ground to capture and store rainwater from the roof. These tanks are typically equipped with filtration systems to ensure water quality.
-
Green Roofs: Green roofs are roofs covered in vegetation that absorb rainwater and reduce runoff. The collected rainwater can be used for irrigation or other purposes within the building.
-
Permeable Pavements: Permeable pavements allow rainwater to infiltrate into the ground rather than run off into storm drains. This can help recharge groundwater and reduce flooding.
Case Study: Singapore’s Rainwater Harvesting Strategy
Singapore, a city-state known for its innovative water management practices, has implemented extensive rainwater harvesting systems to supplement its water supply. The country collects rainwater from rooftops and paved surfaces, stores it in reservoirs, and treats it for potable use. Singapore’s commitment to rainwater harvesting has helped to reduce its reliance on imported water and increase water security for its residents.
Conclusion
Rainwater harvesting is a simple yet effective way for urban households to contribute to water conservation efforts and reduce their environmental footprint. By implementing rainwater harvesting techniques, urban areas can become more resilient to water scarcity and promote sustainable water management practices. Whether through rain barrels, rainwater tanks, or green roofs, there are various methods available for households to harness the power of rainwater and reap its benefits.
Sources:
1. https://www.pub.gov.sg/watersupply/fournationaltaps/rainwater
2. https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2019-08/documents/rainwater_harvesting-guide_3-aug-2019_final.pdf